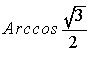 = ____.
= ____.Examples:II. Find trigonometric functions of special angles (in the first quadrant).
If a is an angle of rotation, by definition, sin a = ____.
If A is an acute angle of a right triangle, by definition, tan A = ____.
Given a right triangle (labeled diagram) with two side lengths given, cos A = ____.
Four questions. Two definitions, two evaluations. Students must use the Pythagorean theorem to find the third side of the given triangle.
III. State (17) trigonometric identities. Three Pythagorean; two quotient; six reciprocal; six cofunction.
IV. Change degrees to radians and vice versa.
V. Find trigonometric functions of special angles in all four quadrants and quadrantal angles (in degrees and radians). example
VI. Make quick sketches of the six trigonometric functions.
VII. Find inverse trigonometric function values.
Example:VIII. Make quick sketches of the four inverse trigonometric functions. (Arcsec and Arccsc not included.)= ____.
IX. State the domain and range of trigonometric functions. Five questions selected from the 12 potential questions on each version of the quiz. Students required to use the multiple notation. For example, {x | x real, x <> p/2 + kp, k an integer}. example1, example2.
X. Solve a trigonometric equation.
XI. Solve two right triangle trigonometry problems. Calculator required.
XII. Solve oblique triangles. Two questions. One requiring Law of Cosines, one requiring Law of Sines.
James R. Olsen, Western Illinois University
E-mail: jr-olsen@wiu.edu
created Feb. 2005